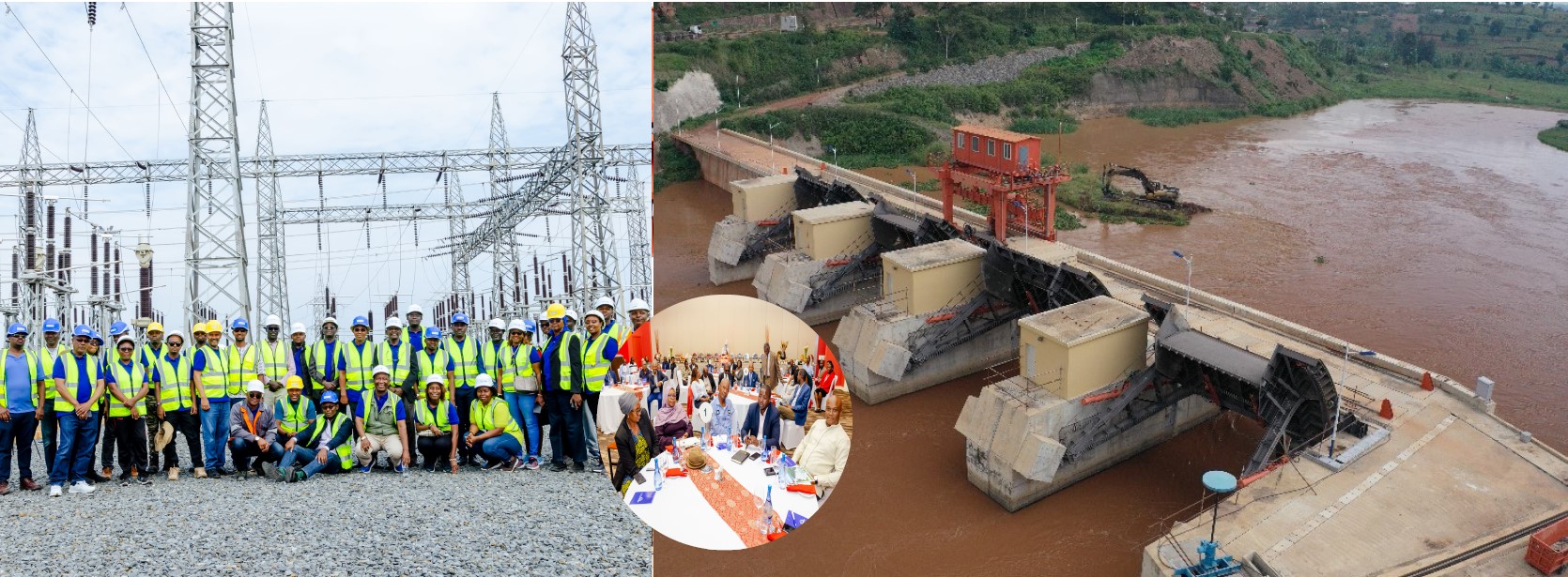
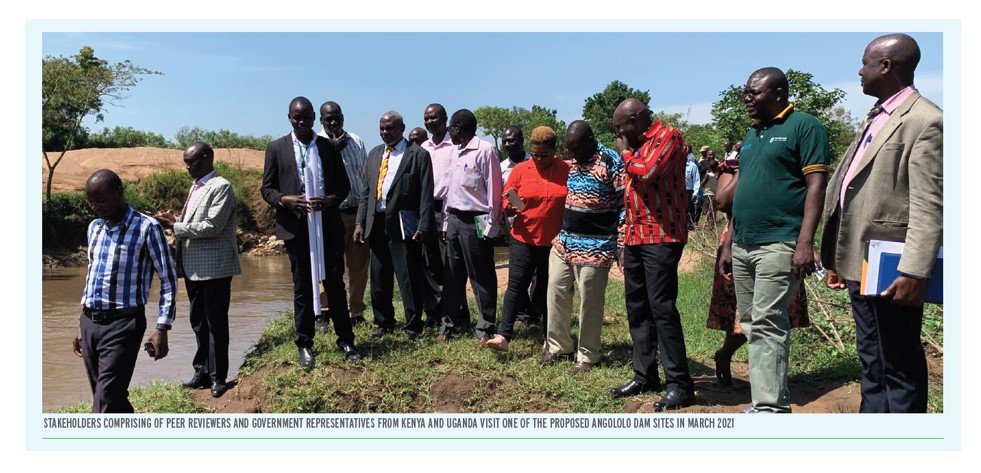
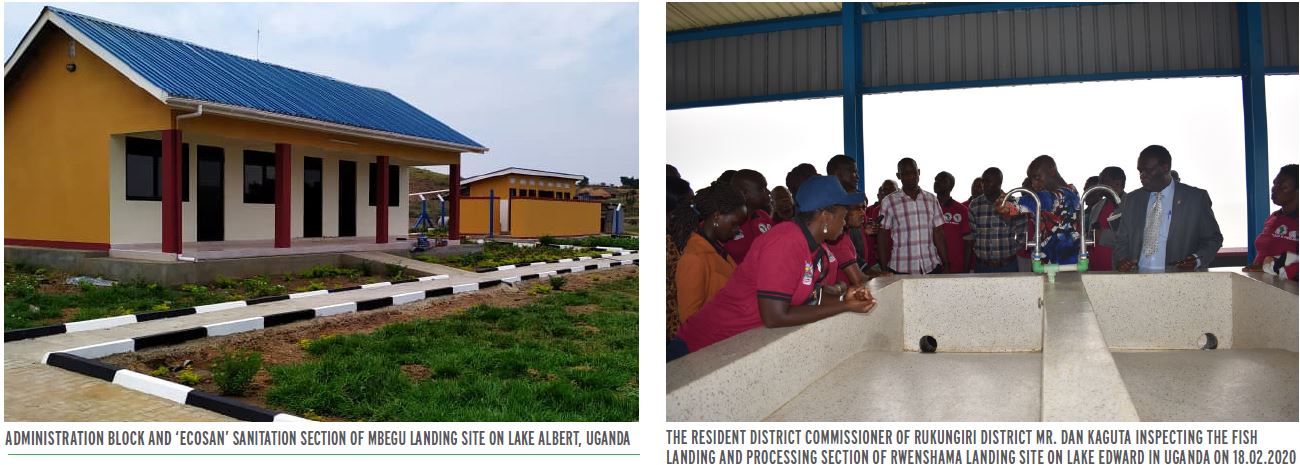
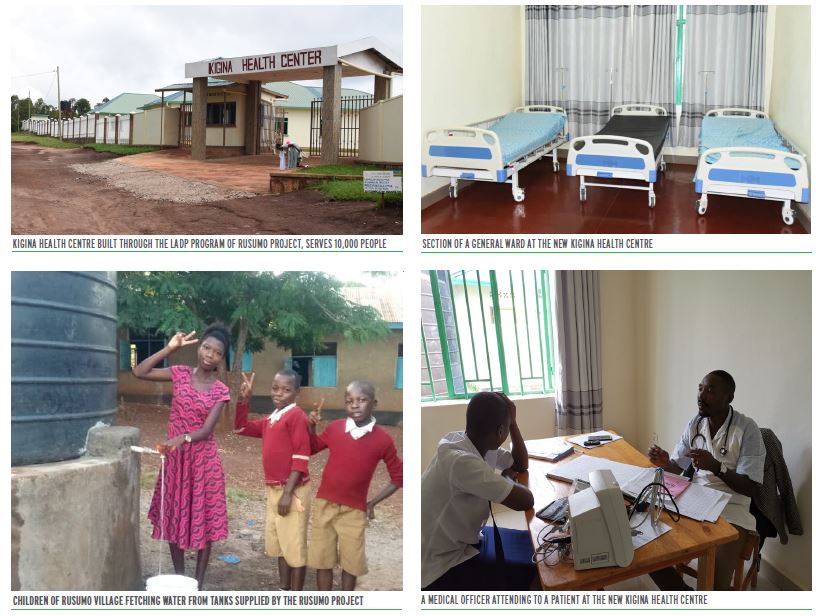
The Cooperative Framework Agreement (CFA) on the Nile River Basin outlines principles, rights and obligations for cooperative management and development of the Nile Basin water resources. Rather than quantifying 'equitable rights' or water use allocations, the Treaty intends to establish a framework to promote integrated management, sustainable development, and harmonious utilization of the water resources of the Nile Basin, as well as their conservation and protection for the benefit of present and future generations. The CFA envisions formation of a commission called the Nile River Basin Commission (NRBC) that will promote and facilitate the implementation of the CFA and facilitate cooperation among the Nile Basin States in the conservation, management and development of the Nile River Basin and its waters.
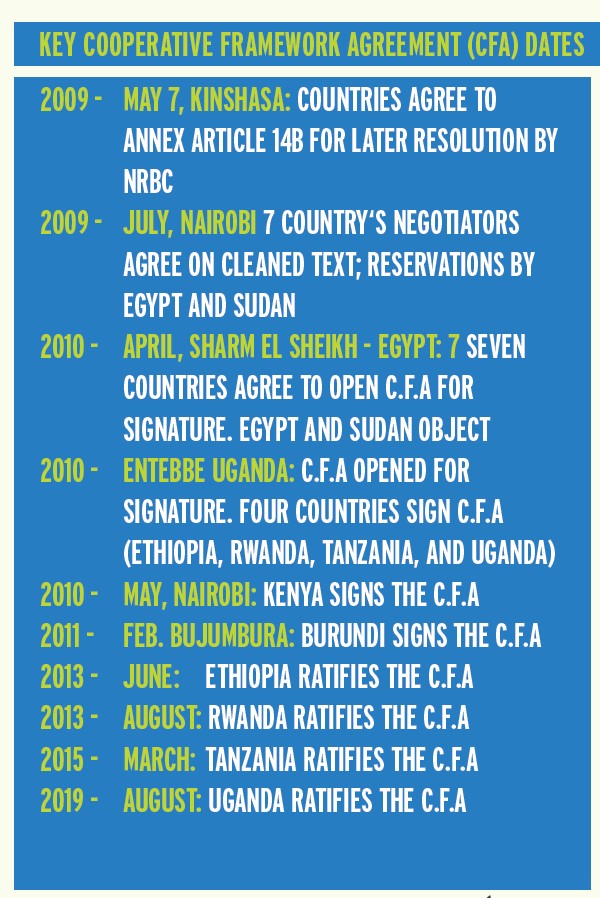
 Evolution of the CFA treaty - negotiation process
Evolution of the CFA treaty - negotiation process
The text of the Cooperative Framework Agreement (CFA) was developed over more than a decade of intensive work by a Panel of Experts, a Transitional Committee, a Negotiations Committee and Technical Advisory Committee (TAC) members. A draft CFA text was submitted to the Council of Ministers of Water Affairs of the Nile States (CoM) in March 2006. The COM members completed their negotiations of the CFA on June 25, 2007, with all but one reservation lifted (Article 14b). The final decision by the COM was to refer the said reservation to their Heads of State summit for resolution.
May 22nd, 2009, Kinshasa, DRC: 7 member countries agree to annex Article 14b for later resolution by NRBC; with reservation by Egypt.
Jul 3rd, 2009, Nairobi- Kenya: During a Meeting of country negotiators 7 countries agree on a cleaned text; with strong reservations by Egypt and Sudan.
April 13th, 2010, Sharm el Sheikh - Egypt: 7 countries agree to open CFA for signature. Position rejected by Egypt and Sudan.
May 14th, 2010, Entebbe Uganda: CFA opened for signature. Four countries (Ethiopia, Rwanda, Tanzania, and Uganda) sign the opened CFA.










































































